
Sep 27, 2019 | Press Releases, Uncategorized
Odyssey Capital Group is expanding our External Asset Management (EAM) Platform and we are actively inviting experienced Private Bankers and Wealth Managers to establish their own wealth practice.
ROLE SUMMARY:
You will be responsible for bringing in new accounts and developing AUM. Cross-selling a wide range of private banking and wealth management products and solutions to clients will be part of your core responsibilities.
Private Client Advisers at Odyssey develop deep client relationships in order to thoroughly understand the client’s situation and utilise that knowledge to develop tailored wealth management strategies. The Advisers are able to add value to individual and corporate clients by building and drawing upon a network of internal resources, often global, to achieve desired results. Successful Advisers are able to develop and adopt a disciplined sales process to convert a pipeline of prospects into target market clients. In addition, they are able to deliver quality client relationships (solutions and services) in an intensely competitive fragmented market, taking advantage of the Odyssey platform while protecting the client/firm by complying with relevant policies, procedures, and country legal/regulatory requirements.
Markets covered: Greater China – Hong Kong, China, Taiwan.
The ideal candidate is an existing private banker and has at least 60%-70% of his/her key clients domiciled in the countries covered. Other candidates and client coverage may be considered.
ROLE REQUIREMENTS:
New Client and Business Development
- Grow client net revenue annually in core product areas: investment management, capital markets, real estate, and banking & lending.
- Create sales and marketing strategies designed to generate revenue growth and to acquire new target clients within different sectors.
- Prospecting – generate leads and develop prospects, network to identify referrals to new clients/prospects.
- Profile, qualify and convert prospects into clients.
- Identify and execute on new business opportunities with existing clients.
- Orchestrate appropriate specialist resources to develop tailored, long-term solutions for clients/prospects.
- Present and communicate to clients/prospects complex financial concepts and investment strategies in a way that is easily understood.
Relationship Management
- Serve as the client’s advocate and trusted advisor (primary contact) for strategic advice on financial matters.
- Create, organise, and implement a wealth management strategy designed to deepen relationships with existing clients.
- Manage client expectations regarding service and deliverables.
- Ensure financial strategies are kept current and appropriately aligned with client objectives.
- Understand and communicate the risk involved with financial and investment strategies.
- Ensure all client inquiries and problems are handled effectively and resolved.
- Help team members to acquire experience and establish credibility with clients.
Compliance Oversight and Controls
- Comply with all regulatory policies and control procedures regarding client transactions and suitability.
- Oversee and ensure clients are on-boarded appropriately including all required documentation is complete and accurate.
Experience
- 3 to 5 years minimum industry experience.
- Established client base with existing AUM.
Qualifications
- SFC or MAS licensed.
- CWM or other designation a plus.
Languages
- English, Mandarin (preferred), Cantonese (preferred).
Roles Details
- Primary Location: Hong Kong or Singapore
- Schedule: Full-time
- Education Level: Bachelor’s Degree or higher
YOUR BENEFITS
- Flexible
- Better Economics
- Tailored Fees
- Equity Participation
- Full Support
- Investment Advisory Desk
- Deal Flow
- Tactical Ideas
- Unrestricted View
- Large Range of Providers
- Independent
- Scale
- Fun Culture
YOUR CLIENT BENEFITS
- Competitive Pricing
- Broader Access
- Research
- Buy Ideas
- Discretionary Portfolios
- Investment Advisory
- VIP Client Events
PRODUCTS
- Discretionary Portfolio Service
- Bespoke Portfolio Mandates
- IPO Allocations & New Bond Issues
- Real Estate Opportunities
- Co-Investment Opportunities
- Differentiated Investment Funds
- Mortgages
- Insurance Solutions
- Institutional Solutions
PLATFORM FEATURES
- Open Architecture, Access & Pricing
- Full Product Suite including Credit Facilities
- 24 hours Trading Platform
- Online Access
- Investment Advisory Desk
- Research Desk
- Multi Valuation “Balance Sheet” Solution
- Full front, Middle and Back Office Support
If you would like to apply for the role, or have questions, contact us here.
About Us:
The Odyssey Group Ltd is Asia’s leading international Alternative Asset Manager providing differentiated and bespoke investment solutions across multiple asset classes, including alternative credit, real estate, private equity, and hedge funds. The Firm’s primary focus is to seek out undervalued investment opportunities to co-invest with its clients.
The Odyssey team comprises over 40 experienced asset managers, lawyers, private bankers, trust & tax planning specialists and experienced investors, each with an average of 25 years of financial, execution and operational experience across the Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America. This experience allows the Odyssey team broad regional industry expertise, insight into global macro and geopolitical trends, and a powerful network of global relationships. When clients partner with the Odyssey Group of companies, they benefit from the breadth and depth of expertise with the entire firm working in unison to achieve a targeted outcome. Our innovative approach allows us to generate attractive investment returns within the context of a prudent and long term horizon.
Odyssey employs the highest quality people as partners in our business while pursuing the highest standards long-term and aligning our interests with our investment partners. It is our mantra to be the ‘trusted partner’ for our clients’ needs.

Sep 16, 2019 | Articles, Global Markets Update
August was, as expected, a tricky month for risk assets as geopolitical issues continued to sway markets, forcing investors into safe-haven assets amid escalating trade tensions, the Brexit debacle, and a string of weak macroeconomic data releases. Equity markets were red across the board, led lower by Emerging Markets (through the MSCI Em Index) which sold off by more than 5% MoM on global growth concerns as investors de-risked and made a flight to safety. The FTSE 100 also declined by as much, as risks of a ‘no deal’ Brexit grew, while the HSI suffered the most, falling close to 7.4% MoM amidst the ongoing protests. Conversely, US Treasuries rallied with 10Y bond yields falling steeply from 2.014% to close the month just as 1.496% – just under a key 1.5% support albeit recovering above that level in the first few days of September. Gold also climbed as safe-haven assets rallied, but oil swung around US$60/bbl with one downside risk remaining the fast expansion in US shale output seen to rise by another 4.5mm/bpd by YE23.
Markets were not helped either by the surprise contraction in the US’ ISM Manufacturing index, which fell unexpectedly to 49.1, the lowest level since Jan ’16. Whilst consumer data remained relatively solid (in particular, robust household consumption), August did see a steep decline in consumer sentiment with the index falling to its lowest since Oct ’16. On a global scale, we saw contractions in the manufacturing sectors across Europe and Asia, and more markedly so the former, which also saw weak sentiment after Germany’s ZEW index fell to it lowest since December ’11.
On the trade front, we saw a sharp decline of retaliatory moves on both sides, with the most recent round of tariffs imposed by the US notably hitting a significant number of consumer goods. China has been reportedly preparing for their own ‘no deal’ scenario on trade, despite earlier concessions to buy 12mn tons of soybeans from the US this year, and this was not helped by the fact that the US also approved a major arms sale to Taiwan, which some see as a ‘red line’ that may have been crossed.
The Fed’s FOMC meeting minutes also came in less ‘dovish’ than markets had hoped, with broad consensus that July’s 25bps cut was more of an ‘insurance’ one, although views are clearly mixed. Powell indicated at his Jackson Hole speech that the Fed would ‘act appropriately’ to extend the US’ economic expansion, which many took as a sign that the Fed would indeed pander to markets should the need arise. He did, however, allude to a flatter Philips curve, implying that inflation was likely to remain low even if labour markets were to improve. This implied that ‘interest rates will run, on average, significantly closer to their effective lower bound.’
It was a likewise rocky month for currencies, with the decline in USDCNY this month, the worst since ’94, while rising ‘no deal’ Brexit risks weighed on the Pound. A string of weaker macro data releases – notably manufacturing data ‘ was not particularly helpful either. The big question is whether consumer spending stays on course, helping to prop up the economy and thus implying a rebound in global manufacturing. More worryingly is the case where this does not happen, consumption fails, in turn sharply increasing recession fears.
Outlook
Trade continues to deteriorate, but it is starting to look like Trump may need to strike a deal before it starts to compromise his re-election efforts. This suggests that we could see some headway in negotiations sometime in H2CY19. However, data out of China suggests that reflation might be coming through and underpinning the economy, which also makes them an unlikely party that might cede a compromise. It is thus a question of where the Yuan goes, as trade might get worse before it gets better. MS thinks that the >5% fall in CNY is a key move which may help offset US tariffs. They estimate that if all US tariffs are implemented by YE19, it will hit China’s GDP by -80bps which can be offset by a 10% decline in CNY which should boost GDP by c. 30bps. On top, much of the damage would be to US importers, retailers and consumers, and if the US moves to impose 25% on all Chinese imports, we could see a US recession as early as 3Q20 which would be a key period for the US elections.
A reluctant Fed has found itself in a difficult position with the FI markets expecting a rate cut versus what their intentions might instead be. As the Fed dislikes ‘surprising’ markets, Powell will either need to forewarn markets that the Fed is more ‘hawkish’, or give in. Should the Fed choose not to cut rates this month, the risk is that longer duration US Treasuries and IG bonds could selloff hard, as might equities.
In Hong Kong, Carrie Lam has finally caved in by offering to withdraw the controversial Extradition Bill. The question then is whether this is enough to dampen down the violence of the protests, with the danger being that it will not, as the focus grows increasingly more on universal suffrage. This raises the risk that a thus far patient Chinese government will crack down harshly ahead of Oct 1st – a symbolically important date which marks the 70th anniversary of CCP taking power in 1949. In our view, it might be too early to bet on sold down HK equities.
We remain underweight Equities but prefer to stay in high-quality US names with defensive characteristics. Within the US, we still prefer growth stocks (in particular, Tech), although we would avoid social media names that appear to face increasing regulatory risks (i.e. Facebook, Google). We prefer holding cash in USD and have an overweight in Alternatives. We also prefer to keep our underweight in Fixed Income, whilst acknowledging that we have missed rally in US Treasuries so far this year. We prefer to remain cautious in this area as our view is that yields do not reward the current risk undertaken. Likewise, we have shifted HY holdings to a minimum, as a severe risk-off event could derail this space and our view is that a selloff here if it does happen, could be particularly painful.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Equities
Equities
-
Equity markets in the US saw a steep decline earlier in the month, recovering briefly only to be rocked by a combination of weak manufacturing data and the continued escalation of Sino-US trade tensions. The S&P 500 traded mostly rangebound between 2,940 and 2,830, closing -1.81% lower for the month. The Dow was down -1.72% MoM, while tech stocks suffered, and the Nasdaq fell -2.60% MoM (Fig 1).
Fig 1: YTD performances of US indices. Source: Bloomberg
-
Within![]() the S%P 500. Energy shares underperformed on the back of weak oil prices, which fell as a result of lower demand expectations after macro data pointed to a slowing global economy. Similarly, financials also fell significantly as expectations of a rate cut cycle grew. Thus, we saw a rotation into defensives like Utilities, Real Estate, and Consumer Staples which outperformed (Fig 2).
the S%P 500. Energy shares underperformed on the back of weak oil prices, which fell as a result of lower demand expectations after macro data pointed to a slowing global economy. Similarly, financials also fell significantly as expectations of a rate cut cycle grew. Thus, we saw a rotation into defensives like Utilities, Real Estate, and Consumer Staples which outperformed (Fig 2).
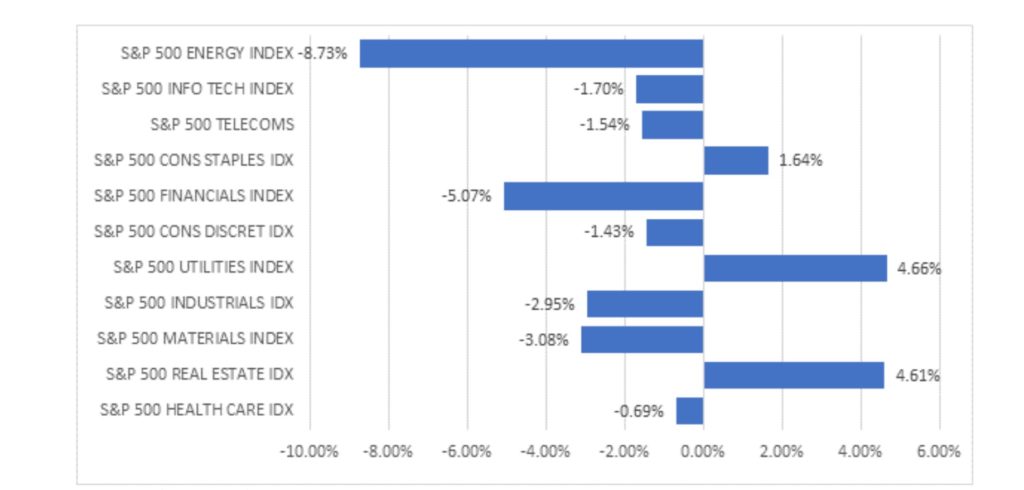
![]() Fig 2: Performace of S&P 500 sectors in August. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 2: Performace of S&P 500 sectors in August. Source: Bloomberg
-
European stocks also declined, albeit somewhat buoyed by an intended rollout of significant easing measures by the ECB. The Stoxx 600 index was down -1.63% MoM, weight lower by Germany’s DAX index (-2.05% MoM), but more so by the FTSE 100 which declined by 5% MoM (Fig 3). Sector performance in the region was similar to that of their US counterparts, with defensives like Utilities (+3.33% MoM) and Real Estate (+2.76%) outperforming.
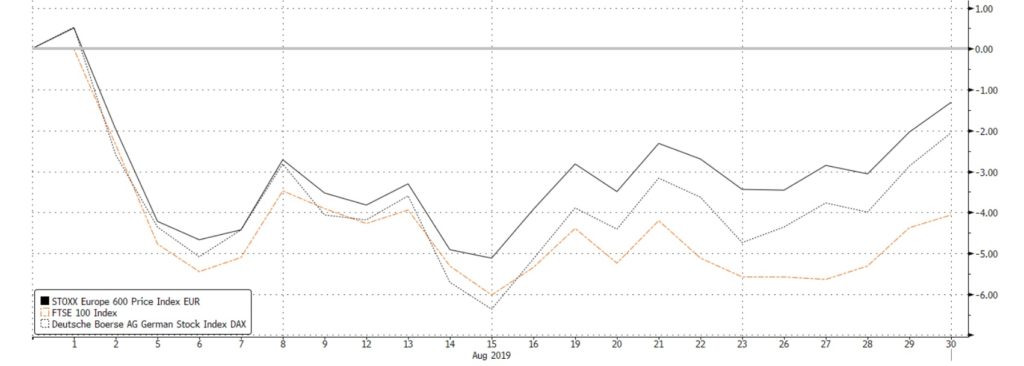 Fig 3: Performance of the SXXP, FTSE 100 and DAX in August. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 3: Performance of the SXXP, FTSE 100 and DAX in August. Source: Bloomberg
-
Stocks in Asia were hard hit by several factors, with EM (MSCI ASEAN fell -4.53% MoM) names seeing a steeper decline, especially those which were more vulnerable to a slowdown in global growth/trade. A-shares (-1.56% MoM) stayed relatively resilient, notably outperforming its large index peers despite the ongoing dispute with the US and weaker manufacturing data. The HSI (-7.39% MoM) was understandably the key underperformer in the region, given the unrest on the streets and mounting concerns that China might be growing weary of staying their hand and choose to intervene more sternly (Fig 4).
 Fig 4: Performance of Asian indices in August. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 4: Performance of Asian indices in August. Source: Bloomberg
Fixed Income
-
US Treasury yields plummeted amid the flight to safety as trade tensions and concerns over global growth weighed in, with the entire yield curve making a parallel shift downwards. 2Y yields fell by 37bps to close at 1.504%, while the 10Y yields saw an even steeper decline from 2.014% to close the month at 1.496% (Fig 5).
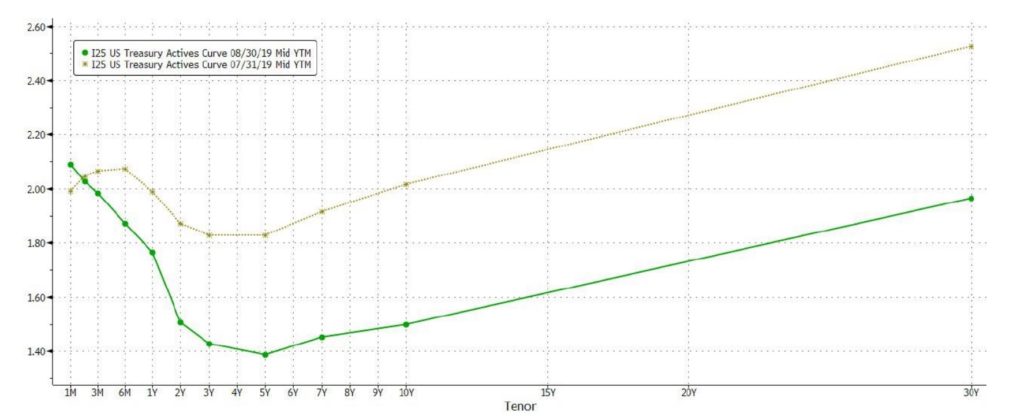 Fig 5: 1M Comparison of US treasury Yield Curve. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 5: 1M Comparison of US treasury Yield Curve. Source: Bloomberg
-
US Investment Grade bonds outperformed, with the aggregate index gaining 3.14%, followed by Asian USD IG bonds which gained 2.41% for the month. Understandably, EM Local Currency Debt declined by -2.00%, while globally, prices of HY bonds fell by -1.56%. CCC bonds in the US also suffered, losing -1.88%.
-
August saw a number of major banks lowering bond yield forecasts, with the HSBC slashing US10YT estimates to 1.5% at YE19 from an earlier 2.1%, and 10Y Bund yields to -0.8% from an earlier -0.2%. Similar moves were made by JP Morgan and Goldman Sachs, the latter trimming its YE19 forecast for US10YT yields to 1.75% from an earlier 2.80%.
-
September is seasonally one of the busiest months for fixed income, with primary issuance in the IG segment set to be as high as $125b according to a preliminary survey of dealers. Although IG spreads have widened significantly since early August, demand looks to remain strong after we saw a month of record flows into IG bond funds.
FX
-
The FX market continues to be driven by geopolitical events (Fig 6). August saw retaliatory actions taken by both the US and China, signaling yet another escalation between the two nations. Brexit ‘clarity’ continues to drive the Sterling as market participants unwound short positions as parliament lowered chances of a hard Brexit. The EUR rose in tandem with the Sterling, aided by the possibility of ‘QE 2.0’ which was sparked from the steady stream of deteriorating industrial and manufacturing data. These factors caused both the EUR and the Sterling to dip below key support levels of 1.20 for the Sterling and EUR’s 1.10.
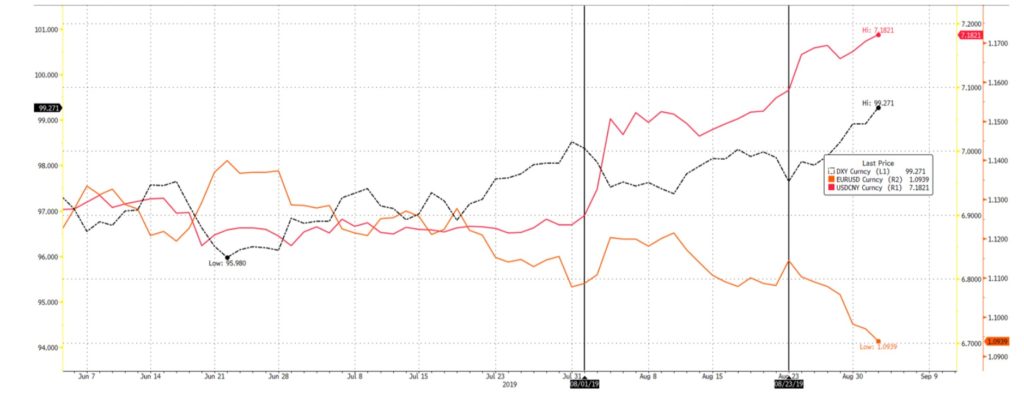 Fig 6: Tariffs are still the main source of activity for FX. New tariffs highlighted by black vertical lines. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 6: Tariffs are still the main source of activity for FX. New tariffs highlighted by black vertical lines. Source: Bloomberg
-
CNY weakened 4.34% from 6.88 t0 7.18, the EUR fell 1.31% from 1.1070 to 1.0940 after it managed to touch 1.12 and GBP fell 1.50% from 1.2150 to 1.1970 and managed to trade to a monthly high of 1.23 on short squeezes. It is worth noting that 1.20 is a 2.5-year support for the Sterling. This caused the DXY to extend its yearly highs from July to touch 99.130 on the 2nd of September. This G7 volatility is to remain at ‘elevated’ levels relative to the first half of 2019.
-
Positioning wise, GBP is now highly net short with over -100k net contracts, the largest it experienced since 2018, and JPY is now net-long since the beginning of August. We currently see room for GBP to rise further, simply on the fact that 1.20 remains a strong support and provides an opportunity for a short squeeze. With net shorts at a yearly high, the unlikelihood of a no-deal exit increasing along with the help of the EUR (aided by temporary CNY strength), we believe that GBP may reach 1.25. Should tensions continue to ease, we see GBP, AUD, as well as major export-based FX pairs (THB, KRW, and TWD) to continue to gain (Fig 7).
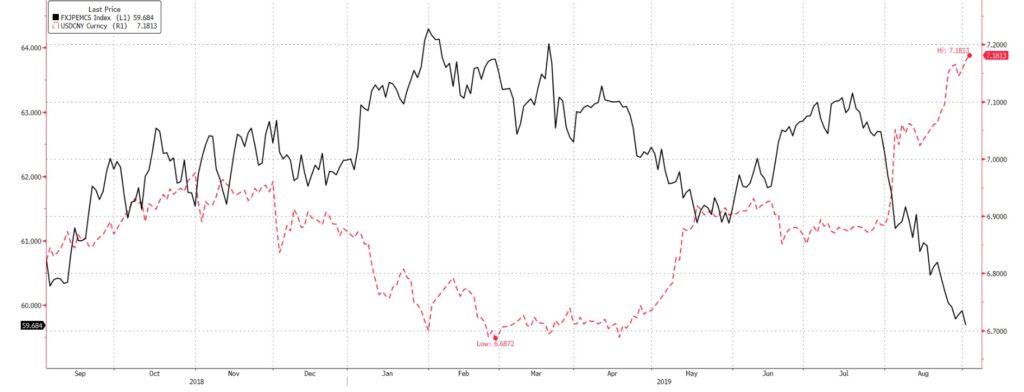 Fig 7: The CNY remains the primary driver of AXJ currencies. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 7: The CNY remains the primary driver of AXJ currencies. Source: Bloomberg
Commodities
-
Brent fell below a key psychological/technical support of $60/bbl as Trump added new tariffs on Aug 1st, adding to fears of a slowdown in global growth. The announcement of tariffs caused the Brent price to dip from $64.10 to $56 and Gold saw a rise from $1413 to $1550 (Sep 4th). China’s retaliatory response on Aug 23rd added even more downside pressure. Brent ended the month slightly lower at $59 and maintained a short-term trading range between $61.30 and $58, after recovering from $56. Gold still maintains a strong upwards momentum as its previous resistance has now become a support (Fig 8).
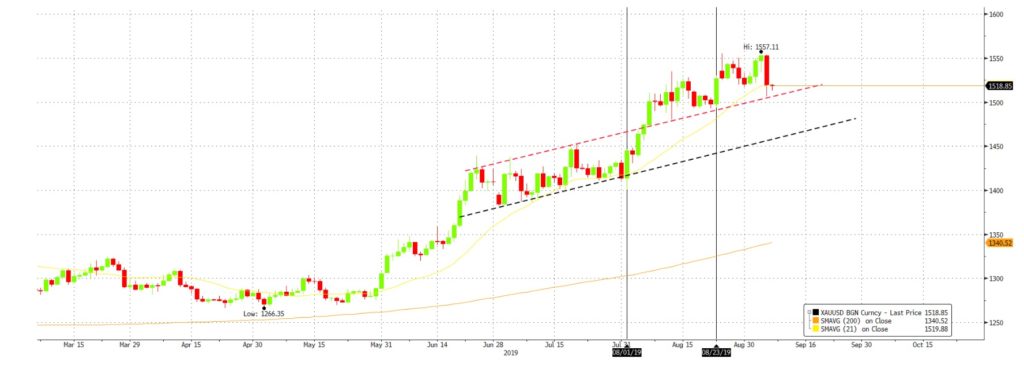 Fig 8: Gold’s momentum is supported by tariffs. Its previous resistance is now a support. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 8: Gold’s momentum is supported by tariffs. Its previous resistance is now a support. Source: Bloomberg
-
The trading range is caused by a few factors; global refinery outages fell to seasonal nine-year lows as they front-loaded 2019 maintenance cycles in preparation for IMO 2020 rules; OPEC’s output rose for the first time since its commitment to dent supply, due to Russia’s 1.2% gain in output (this comes before their re-commitment on the 4th Sept); Hurricane Dorian, the first Cat 5 major hurricane of 2019, which if foreseen to impact the Gulf of Mexico.
-
For September, we see Brent’s $58 to hold as a support and for the 200DMA at $64 to be tested. With freshly added tariffs and further interactions to be had with President Xi and Trump, we believe that this familiar phase of non-aggression should allow other short-term factors to push the price of oil higher in the interim. This includes the return to commitments cut from Russia to cause a further slowdown in OPEC supply, and for Hurricane Dorian to reach the Gulf of Mexico and thus dent production.
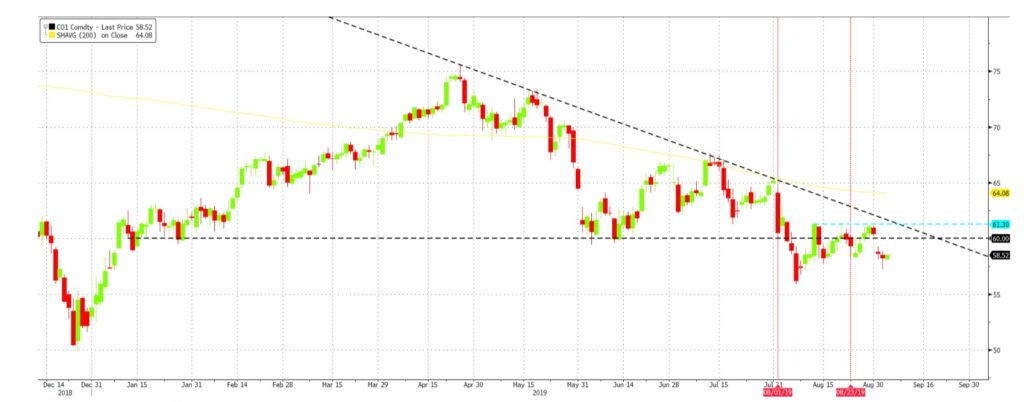 Fig 9: Retaliatory tariffs have pushed oil lower, whilst OPEC supply kept prices buoyant. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 9: Retaliatory tariffs have pushed oil lower, whilst OPEC supply kept prices buoyant. Source: Bloomberg

Aug 22, 2019 | Articles, Global Markets Update
Last week saw the heaviest sell-off in the S&P 500 (the worst since Dec ’18), with US indices seeing sharp pullbacks into early August just shortly after making fresh all-time highs in the last week of July. A re-escalation of Sino-US trade tensions, as well as a pullback in rate cut expectations (with market expectations of a rate cut cycle against Powell’s comment that this month’s move was more of an ‘insurance’ cut), were key factors contributing to the decline in risk-on assets. Likewise, weaker-than-expected data releases globally added to concerns over the state of the global economy, bringing oil down below its key US$60/bbl support despite the worsening relations between the US and Iran. Economically, the US continued to display relative resilience compared to most other major developed markets, understandably outperforming as the S&P 500, Dow Jones and Nasdaq gained 1.31%, 0.99% and 2.11% in July. This was in comparison to the Stoxx 600 (+0.23% MoM) which was buoyed by better-than-expected (albeit heavily downgraded) earnings releases, and Japanese equities in the Nikkei 225 (+1.15% MoM) which saw a pretty decent month. The MSCI Asia ex-Japan (-2.17% MoM), however, underperformed significantly as Chinese equities tumbled on weak data and the trade spat, with A-shares falling -1.55%, and amid the ongoing protests in Hong Kong which undoubtedly weighed on the HSI (-2.68% MoM). The YTD rally in Indian equities also came to an end, with the Sensex (-4.86% MoM) coming off all-time highs to be the underperformer for the month.
What was mostly a calm month for currencies (with the exception of Boris Johnson’s election and steep moves in GBP) soon turned into a storm after Trump surprised markets with his additional imposition of tariffs on Chinese goods. The DXY surged to a YTD high of 98.900 on Powell’s comments before retreating back to 97.220, while in early August, retaliatory moves by the PBoC saw onshore CNY quickly fall below the key psychological Rmb7.0 level. Prior to that, the Euro was mostly led lower by a weaker Sterling on renewed hard Brexit concerns and Boris’ loss in the by-election which nipped away at whatever was left of the majority vote that he had.
Outlook
The sudden shift in sentiment brings back memories of the plunge in Q4CY18, and in particular, the heavy selling during December towards Christmas Eve. Markets have discounted much of the good news – from better-than-expected (albeit post-downgraded) earnings, the ‘dovish’ pivot by the Fed and global central banks, the trade ‘truce’ as well as a moderation of geopolitical risks in the short-term – to the point that Morgan Stanley thinks 22 other central banks will join the Fed in cutting rates by YE19. H2CY19 will potentially be much rougher as geopolitical risks are rising with 1) a ‘no deal’ Brexit 2) dysfunctionality in Spain 3) Italian opposition to EU’s fiscal rules and a possible election giving Salvini control 3) greater Russian adventurism 4) a brutal crackdown on HK’s protesters 5) rising tensions around the South China Sea, Taiwan, 6) worsening tensions between Korea and Japan and 7) rising tensions in the Middle East alongside 8) the instability of Trump.
We have deliberately held an underweight equity positioning and high cash levels for much of this year, more so since April and that worked in May but was impacted by both Powell’s end-May ‘pivot’, and renewed hopes of a trade ‘truce’. We stuck with our defensive positioning as we feared that the optimism in markets (not least as Forward P/E’s on the S&P 500 pushed through 17.5x) was not justified, although the Fed U-turn in November despite robust macroeconomic data (in particular, consumption) caught us out. I see the potential for this correction to run c. 10-15% more, with the S&P 500 re-testing 200DMAs at 2,770 as other, more trade-vulnerable markets to suffer more. EM/AXJ markets are more at risk, not just to trade-related damages, but also to a stronger USD. I struggle to find enthusiasm for US Treasuries, having missed the rally and as the yield on 10Y US Treasuries, below 1.8%, are giving you a negative real interest rate & prefer cash. Our trades into gold found vindication (clearly Bitcoin would have been better!), but we doubt that prices can run much further through key resistances at $1,450-60/Oz.
We remain cautious around risk assets and prefer holding cash in USD. Any major correction offers a trading opportunity to rebuild riskier assets – notably quality equity franchises as Visa or Diageo. In the near term, we could see volatility spike up across most asset classes. Helmets on. The elixirs that could soothe markets might also bring about some damage to capital markets; the Fed moving into a rate cutting cycle; Trump, fearing his trade policies might cost him the election, could ease off on tariffs on China; Powell’s complete U-turn in monetary policy despite US macro data remaining solid, can only be explained by a pandering to please capital markets. On this note, any fall of 10%+ (as we saw in December last year) will likely move a Powell-led Fed to exercise the ‘put’ option that markets expect. This probably sets the lower range of any selloff in the S&P 500 to around 2,630 – 2,770 (Fig 1), which is not unlikely given our expectation of both earnings & GDP downgrades, as well as potential damage caused by trade tensions and geopolitical worries.
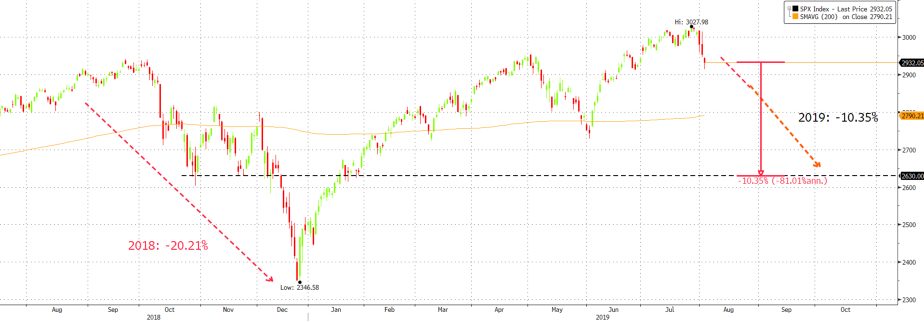
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Fig 1: SPX projected to test a mid-term support of 2,630 Source: Bloomberg
The US, The Global Economy and Powell’s ‘Put’
US GDP data is always distorted between Q1 and Q2. It is clear the huge jump in 2Q19’s consumption numbers after a weak Q1 was in part carried over from the previous quarter (the US government shut down may have had an impact) but nonetheless, it was robust and reflects solid consumer sentiment surveys. Q2 was also impacted by destocking in inventories that had boosted Q1. By stripping these out, the likely underlying GDP growth in Q2 was c. 3% relative to Q1’s 2%. Government spending, buoyed by the Trump fiscal boost of $1.5trn, accelerated but this will slow down in Q3 and fall off a cliff by Q4CY19 as the new fiscal year kicks-in. Business fixed asset investments and net trade were negatives. All in all, this was a solid quarter underpinned by consumption, which accounts for 70% of the US’ GDP. The strength in consumption is at odds with the caution corporates are providing, via a negative-to-positive forward guidance ratio of 3:1 for H2FY19 earnings, and their reduction in capital expenditure. With unemployment at 50Y lows, accelerating wages (private sector wages, including perks, are rising at over 4% p.a.), low mortgage costs and confidence around job security; there is a decent argument that the consumer, assuming Trump leaves trade tariffs as they are (the next $300bn of US tariffs on Chinese imports would mostly hit consumer related items), will remain resilient in H2CY19 (the latest Conference Board survey was very strong). If so, then the ‘gap’ between consumer optimism and corporate caution (if not FI markets’ pessimism) might close in favour of the consumer, implying upside to US domestic demand, GDP growth and earnings growth in the S&P 500. Of course, the risks for corporates include a strong labour market (which will drive up employment costs more quickly and so impacting margins), along with trade-related damage and a higher USD.
For us, what is quite clear is that the Q2 GDP data, recent NFP, consumer sentiment surveys, and durables, along with US equity indices close to all-time highs, do not provide the reasons for the Fed to cut rates – indeed Professor Shiller rightly suggested the current conditions in the economy and capital markets support the argument more for a rate hike than the Powell ‘put’ of a rate cut we experienced. Clearly, the Fed is pandering to capital markets and the critic-in-chief, Trump. Resilient consumption and, as a result, better S&P 500 earnings, may support the index’s rally to break firmly through 3,000 (GS’s revised price target is 3,100), but it might limit the Fed to a one-off rate cut, boost inflation and underpin US GDP growth and USD. We continue to see more downside risks from rising geopolitical scenarios (‘no deal’ BREXIT, Iran confrontation, worsening Japan-Korea trade spat, South China Seas tensions, US’s possible sale of F-16s to Taiwan in Q4 which is a redline for China, political risks in Italy and Spain and risks around Turkey and South Africa). In addition, IMF recently cut global GDP growth forecasts in both CY19 and CY20, with the bulk of these downgrades coming from the BRICS.
Frankly, it is very difficult, we find, to have a strong conviction on the outlook and that means capital markets could be prone to violent, large moves and spikes in volatility as we have just seen. But with Nasdaq still up c. 15% YTD and double-digit gains in the MSCI ACWI, the odds suggest going more defensive in portfolios by reducing riskier assets like equities (with US stocks on expensive valuations), and high-yield FI (forecasted default rates are moving up), but we will be monitoring US consumption positives as well as the degree of monetary easing we get by the Fed alongside the other 22 central banks globally (MS thinks that they will cut rates by YE19). Our basic thesis is risk assets have discounted a lot of the positives yet are ignoring the negatives at a time when the rally in sovereign debt implies a dichotomy on outcomes – one, or other, of these two asset classes, will sell-off hard.
Re-escalation of Sino-US trade tensions
Last year, China’s move to allow the CNY to depreciate from 6.23 to 6.98 had ‘neutralised’ the initial 10% of US tariffs, a move which in part incentivised Trump to impose even hasher tariffs. Indeed, Trump made it clear that the latest 10% on the remaining $300bn of PRC imports (due by 1/9), could be increased to 25% or higher. Whilst China could likewise impose higher tariffs on US imports, it is running out of room and will thus need to find other ways to retaliate. It appears China is taking a tougher line since the earlier breakdown in talks earlier this May, and not compromising on core structural economic objectives. One line of thought here is that despite the trade war and with domestic reflationary policies perking up the Chinese economy, China is emboldened in its negotiating position. Another is that they can live with the ‘pain’ and wait for Trump to be replaced after Nov 20thby a more rational administration. Certainly, the narrative around this Sino-US trade war posits a decreasing likelihood that an accord will be reached before the next US election, with some suggesting that Trump sees a deal as potentially giving Democrats an opportunity to attack him. There are no signs yet, electorally, that the trade war is hurting Trump’s appeal. Having said that, 68% of the latest round of tariffed goods are consumer items, and should Trump increase tariffs significantly further from here, he risks alienating the voters and creating a recession – MS thinks if this extra $300bn of imports were to suffer a 25% tariff, the US economy would go into recession within 6-9M, coinciding with a key voting period in Q2 and Q3 when most make their mind up.
‘Weaponising’ the CNY has long been talked about by bears of the currency, but this has not happened, and most studies still see CNY as at fair value. However, the Chinese lack an obvious trade-related retaliatory measure, so they could, if angered, choose to devalue the CNY by another 5-6% (Fig 2). Fundamentally, China is moving towards both a trade and current account deficit – US surplus is the large exception – so it is not wrong to assume that the CNY might fall further. Bears argue that the currency should depreciate to 7.50-7.60, even 8.00, as this would ease pressure on PBoC from sticking to tighter monetary policy. The principal reason against a major devaluation is that the government rightly fears capital flight that, if extreme, could destabilise its financial system by creating a liquidity run. With capital controls and a stable currency, China can retain sufficient domestic liquidity to ensure that a solvency crisis does not deteriorate into a more damaging liquidity crisis. A major amount of capital fleeing China could force the PBoC to jack up rates precipitating a recession. Financial system defaults – given high corporate debt-to-GDP – alongside capital flight, would only increase the risks. We think it is unlikely that the PBoC and the Chinese government would take this risk, but where the line-in-the-sand is we do not know – it might be here at 7.00 or at 7.20. If we take 6.80 as an average point, then a 5% depreciation from there implies that 7.10-7.20 is feasible. Another factor against a rapid fall in CNY is that China prides itself in the relative stability of the currency, and the benefits that this carries for its vast trading complex. Lastly, if forecasts prove right and China moves into a trade & current account deficit, a weaker CNY would most definitely be negative. If this were to be the case, we would not be surprised if China accelerates its selling of US Treasuries given their YTD rally and the recent moves in CNY.
As the two sides’ trade confrontation spirals further into a toxic standoff, it will damage not just their own but the global economy as well; in doing so adding to more GDP downgrades, notably in the trade sensitive EU where feeble domestic demand and an underpowered ECB cannot offset trade weakness, as well as APAC. It also raises the stakes in that the Sino-US trade dispute is part of a wider strategic confrontation between the two that is just starting. The risks lie in a higher non-trade conflict (as with issues around the South China Seas or the US’ intent to sell F-16s to Taiwan), take on a greater life and further reduce hopes of a trade compromise.
Fig 2: CNH’s room to weaken to 7.35 Source: Bloomberg
Equities
-
The S&P 500 has once again failed to confirm a breakout above 3,000, and it could be that the rally ahead of the Fed’s expected rate cut was the ‘rumour’ helped by a better-than-expected Q2 EPS reading, albeit one that is tracking a negative two-to-three percent YoY earnings contraction for a second quarter in a row. Nonetheless, the correction thus far across US indices has been steep (Fig 3), while other markets are breaking 200DMAs as – in APAC – the STI, KOSPI, and the HSI with others heading there. ![]()
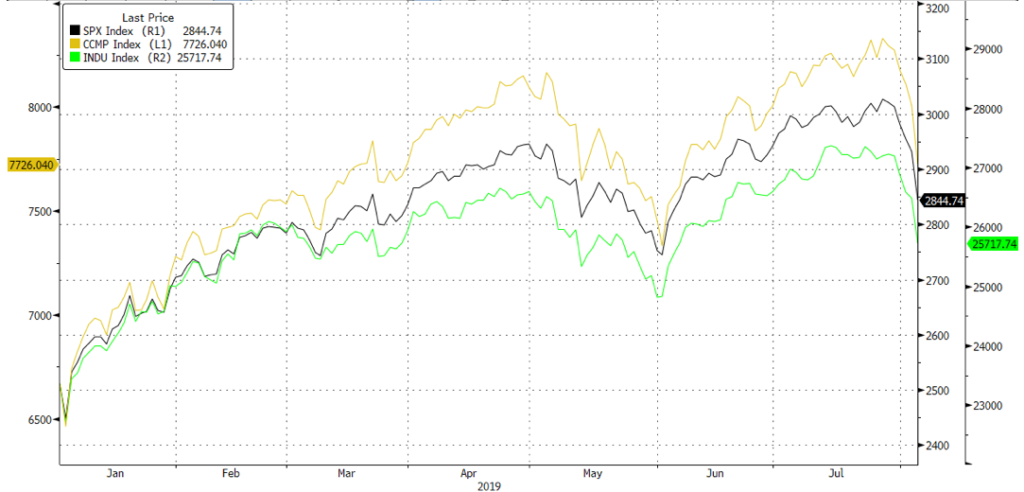
![]() Fig 3: YTD performance of US indices Source: Bloomberg
Fig 3: YTD performance of US indices Source: Bloomberg
-
Q1FY19 earnings for S&P 500 ‘beat’ the conservative consensus by around 3%, falling just -30bps YoY whilst 76% of the 77% S&P 500 companies that have reported Q2FY19 earnings have also ‘beaten’ conservative consensus estimates. Factset thinks that the companies which have reported so far – along with estimates for those to report – will see Q2FY19 earnings fall by -1.0% YoY relative to the -4-5% consensus estimate during the pre-results season. Year-to-date, S&P 500 EPS has been cut by -6.5% from YE18 estimates.
-
The same is true for Stoxx, where Q2 results are seeing a net ‘beat’ over significantly downgraded forecasts after Q1 results were out but will still likely be down -4% YoY on an absolute basis. There is ‘polarisation’ between where S&P 500 H2 earnings will go with consensus (and Goldman Sachs) expecting +3% (GS also forecasts +5% FY20E), which implies a double-digit recovery in H2 and especially in Q4FY19 where comparatives to the FY18 base look easier.
-
This is opposed to others like Morgan Stanley, who see a contraction in overall FY19 earnings, and think that earnings consensus for H2FY19 is way too high, and that might result in the S&P 500 correcting 10%+ as investors become more pessimistic. To the extent that the US consumer looks to be in rude health, the key to growth/contraction in FY19 earnings might lie in whether toplines hold up (helped by stronger consumption spending), and the degree to which corporate operating profit margins are squeezed. One lead indicator for future earnings are today’s sales growth and here the ‘weak-ish’ Q2FY19, in contrast to better than expected earnings ‘beats’, is a downside indicator into H2.
-
In APAC, our overweight positioning in Chinese equities (Fig 4)is starting to look a lot less clever as trade and a depreciating CNY hits the defensive domestic counters like Tencent and Alibaba, as well as preferred names in Real Estate and Financials. Our sense is thus a need to reduce exposures in this region. Meanwhile, domestic troubles are making Indian equities less attractive, while ASEAN is exposed to trade damage and USD strength.
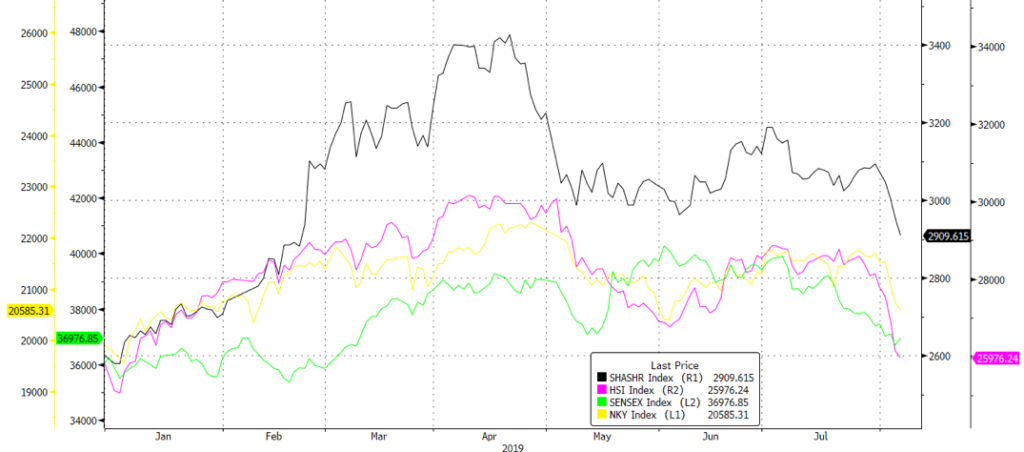 Fig 4: YTD performance of Asian indices Source: Bloomberg
Fig 4: YTD performance of Asian indices Source: Bloomberg
Fixed Income
-
US Treasury (UST) rates were mostly flat in July. While the 2Y yield ended at 1.87%, 11.72bps higher MoM, the 10Y yield was mostly flat at 2.01%. However, yields tanked, and the UST yield curve flattened in the first two days of August after Trump announced the tariffs on additional Chinese imports (Fig 5). Weaker manufacturing data after also weighed on yields. Despite this, we remain convinced that the current economic conditions in the US do not warrant a monetary policy easing cycle.
 Fig 5: Flattening of UST yield curve Source: Bloomberg
Fig 5: Flattening of UST yield curve Source: Bloomberg
-
German bunds yield trended lower throughout July, extending declines from June, as European economic data remained weak. The fall in German yields accelerated in the first two days of August as well, ending the week with the entire German yield curve in negative territory (Fig 6).
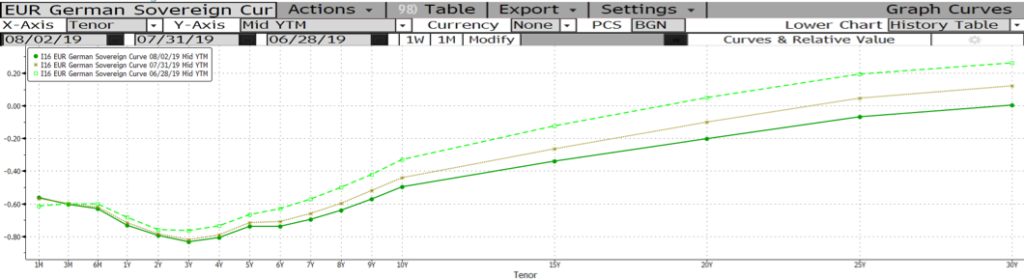 Fig 6: Germany sovereign yield curve falls below zero Source: Bloomberg
Fig 6: Germany sovereign yield curve falls below zero Source: Bloomberg
-
EM debt was the best performer last month. EM hard currency debt, represented by the Bloomberg Barclays EM USD Aggregate index, returned 1.00% while EM sovereign local currency debt (LCD), represented by the Bloomberg Barclays EM Local Currency Government index, returned 0.98%. We continue to favour EM debt, particularly hard currency debt, relative to other FI sectors given the market’s hunt for yield in the current low-interest rate environment. We are more cautious around LCD, especially given the strong dollar.
-
Within corporate credits, high yield (HY) debt generally outperformed investment grade (IG) debt (Fig 7). Both IG and HY index spreads are trading at the lower levels seen in ‘18, with the IG index yield trading at 2Y lows. With IG yields back at that level, we don’t think it justifies the inherent risks and thus prefer HY debt.
 Fig 7: HY vs IG returns Source: Bloomberg
Fig 7: HY vs IG returns Source: Bloomberg
FX
-
The DXY reached a YTD high of 98.90 last week but has since continued to fall since Trump’s renewed tariff threats. Previous resistance levels, bar the 103 peak in end 2016, can be seen at 100 (Fig 8). This is likely the next level of resistance if markets continue to back the dollar on the Fed’s less-than-expected dovishness. We have seen the DXY break through a key resistance of 98.50 over the last week, with support from its 200DMA at 96.93.
 Fig 8: DXY resistance at 100 Source: Bloomberg
Fig 8: DXY resistance at 100 Source: Bloomberg
 Fig 9: EURUSD breaks below key support of 1.11 Source: Bloomberg
Fig 9: EURUSD breaks below key support of 1.11 Source: Bloomberg
-
In our previous monthly, we noted that the flight to ‘safe haven’ currencies could be steep, should trade tensions escalate once again. They did, and we saw JPY gaining to 105.60. We expect haven currencies (JPY, CHF) to see continuedstrength, and for the Sterling to be exposed to the downside in lieu of Brexit uncertainty.
-
Citi’s broad NEER values show the Yuan dipping below 98 with speculation that China will further adjust its real effective rate lower to offset the impact of new tariffs. This will likely put downward pressure on Asian currencies as they adjust to accommodate this pressure. We see an opportunity in shorting the Thai baht, as a weaker yuan might release some of the latter’s strength which we saw in July.
Commodities
-
Last month, we noted a trading range between US$60-68/bbl, based off numerous factors including Trump’s pressure on Iranian production as well as a slowdown in overall demand from trade wars. In July, Brent saw a rise to US$67/bbl, helped higher by the continued momentum of production declines from June as well as an inventory decline for Cushing crude. Hurricane Barry also helped push oil prices higher by shutting down c. 1m bpd of production in the Gulf of Mexico. However, this rise was soon offset in a gradual build of inventory once again as exports slowed from a dip in demand due to trade wars. Short bouts of dollar strength from Powell’s less-dovish comments also helped push oil lower.
-
We adjust our trading range for oil to US$60-$65/bbl, with a bias to the downside, and see the $60 level as a support that may break by the end of Q3. We follow the 200DMA resistance level of $65 and note that the support at $60 has been tested 4 times since June. With the added tariffs from the US, as well as a retaliatory stance from China, we foresee that tensions are more likely than not to rise and this should further dampen the overall mood for risk, and therefore the outlook for global growth.
(Fig 10)
 Fig 10: Brent crude on a downward trend Source: Bloomberg
Fig 10: Brent crude on a downward trend Source: Bloomberg
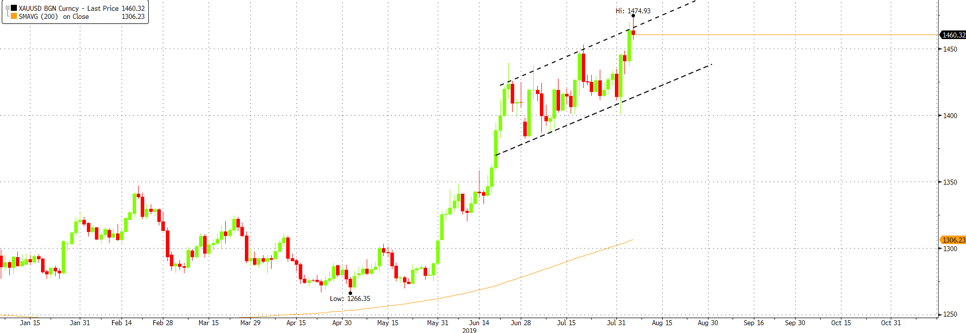 Fig 11: Gold’s upward channel Source: Bloomberg
Fig 11: Gold’s upward channel Source: Bloomberg
-
The increasingly uncertain backdrop has and will likely continue to benefit the precious metal, with the potential for prices to rise above US$1,500/Oz. From a technical perspective, we view Gold’s momentum to be too strong for a “sell-off” reversal, similar to what we saw in equity markets.

Aug 21, 2019 | Press Releases, Uncategorized
Partnerships
Odyssey has recently partnered with New York-based Cadre, a technology-enabled real estate investment platform, to allow Odyssey’s private wealth management clients to invest in Cadre’s syndicated property opportunities.
Cadre leverages technology to make it easier and less costly for individual investors and institutions to buy stakes valued from just US$100,000 USD in institutional-quality U.S. commercial and multi-family real estate. Cadre’s investment opportunities target superior risk-adjusted returns with an emphasis on cash flowing real estate driven by differentiated sourcing, data-driven diligence, increased transparency and flexibility for investors.
Led by CEO Ryan Williams and a team of professionals from premier investment firms including Blackstone, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Dune, and GEM Realty Capital, Cadre has invested in transactions totalling more than US$2.5 billion in transaction value since launching.
Through the partnership, Odyssey’s clients will be able to use Cadre’s platform to select institutional- quality U.S. commercial and multi-family real estate investments vetted by Cadre’s experienced team.
Odyssey’s partnership with Cadre highlights sustained interest by Asia Pacific based clients in accessing institutional-quality commercial and multi-family real estate investment opportunities in the United States.
About Cadre
Cadre is a technology-enabled real estate investment platform that provides qualified individuals and institutions access to fully vetted commercial real estate opportunities. Cadre enables investors to gain exposure to the asset class in a fee-efficient, transparent manner. Cadre has invested in transactions totalling more than US$2.5 billion in transaction value to date and has closed on more than US$130MM in corporate funding from backers including Andreessen Horowitz, Khosla Ventures, Ford Foundation, Thrive Capital, and General Catalyst.
www.cadre.com











 Fig 9: Retaliatory tariffs have pushed oil lower, whilst OPEC supply kept prices buoyant. Source: Bloomberg
Fig 9: Retaliatory tariffs have pushed oil lower, whilst OPEC supply kept prices buoyant. Source: Bloomberg










 Fig 11: Gold’s upward channel Source: Bloomberg
Fig 11: Gold’s upward channel Source: Bloomberg